Git Init Pull
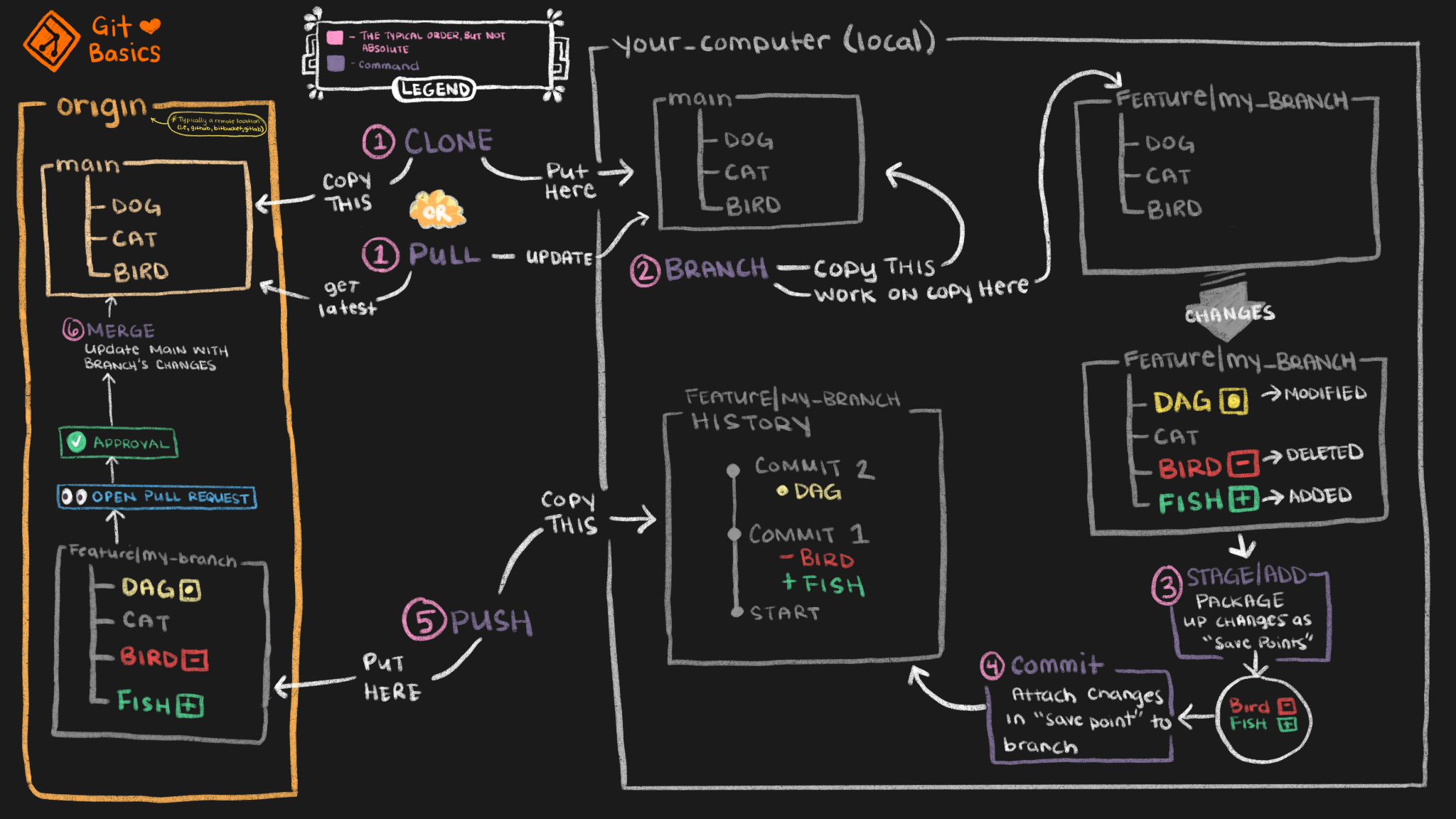
Creating a new git repo is a little more involved than one that is already setup but here are the simple steps to get one rolling. I prefer to use SSH over HTTPS due to security and ease of use from the command line.
Setup
We need to first do a few things to make a commit as easy as possible.
-
Create a ssh key if you haven’t already. This will be placed in ~/.ssh unless you tell it otherwise with the -f flag.
$ ssh-keygen -t rsa -b 4096 or for a more secure and smaller key file $ ssh-keygen -t ed25519 -
Copy your .pub key to your clipboard.
$ cat ~/.ssh/id_rsa.pub or $ cat ~/.ssh/id_ed25519.pub -
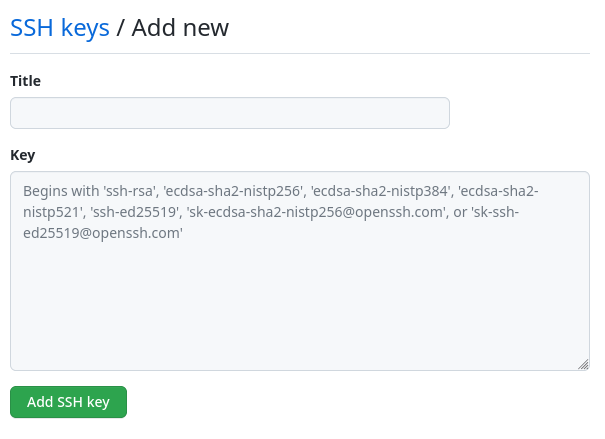
Go to your github page and head to your username icon in the top-right corner and hit settings -> SSH and GPG keys
-
Paste the .pub key into the New SSH Key and add a title name for the key.
-
Next create a new repo by clicking the plus sign -> New Repository in the top left corner.
-
Choose the name you want here and make it either public or private.
- Do not add a readme file or .gitignore nor a license at this time. It only makes it harder on the next steps.
-
Click Create Repository
- Here it will show you the command to run to get the repo initialized and setup but I will show them here as well.
Initialize and commit
-
cd <directory/of/new/project>
-
git init
-
git add .
-
git commit -m “initial commit”
- You might be prompted to verify who you are here. If you are run this below and run #4 again.
$ git config --global user.email "<email used to setup git account>" $ git config --global user.name "<username used on git account" -
git push
Conclusion
You have now setup a new git repo.